CHRONIC TONSILLITIS: CONSERVATIVE AND SURGICAL TREATMENT
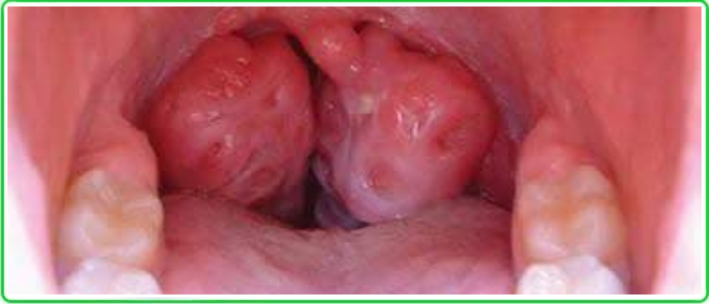
What makes our throat seem as if it belongs in a Tolkien fairy tale like The Lord of the Rings?
It’s the Waldeyer’s lymphoepithelial pharyngeal ring — a unique dual “ring” system of solitary lymphoid clusters that stands guard over our health.
Palatine Tonsils — More Than a Simple Organ
The palatine tonsils are part of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) and perform essential functions:
- first line of defense against exogenous pathogens;
- phagocytosis of foreign agents;
- generation of B-cells (1/3) and T-cells (2/3), crucial for immune response.
Regional lymph nodes: submandibular (more common) and cervical (less common) nodes may enlarge and become tender during an exacerbation of tonsillitis.
Modern perspective: tonsils cannot be classified as “inflamed” based solely on a clinical examination. Their size is not a diagnostic criterion for chronic tonsillitis, but it is clinically relevant if they interfere with breathing or swallowing.
Symptoms of Chronic Tonsillitis
- recurrent sore throat;
- bad breath;
- difficulty swallowing;
- enlarged and tender lymph nodes;
- tonsillar crypt debris (“tonsil stones”);
- general malaise and reduced productivity.
Diagnosis
Includes:
- medical history (frequency of tonsillitis episodes, comorbidities);
- oropharyngeal examination and endoscopy;
- bacterial cultures;
- complete blood count and inflammatory markers;
- ultrasound of lymph nodes if necessary.
Conservative Treatment
- tonsillar lacuna irrigation with antiseptic and antimicrobial solutions;
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- local antiseptics and immune-modulating agents when indicated;
- physiotherapy (laser, ultrasound);
- treatment of coexisting ENT conditions and infection sources.
Indications for Surgical Treatment (PARADISE Criteria)
Tonsillectomy is indicated if:
- ≥7 episodes of sore throat in the last year,
- ≥5 episodes per year for the past 2 years,
- ≥3 episodes per year for the past 3 years,
and each episode is documented and accompanied by: - fever ≥38.3°C (101°F);
- enlarged and tender cervical lymph nodes;
- tonsillar exudate or a positive test for Group A β-hemolytic streptococcus.
Other indications include:
- chronic tonsillitis complicated by peritonsillar abscess;
- severe tonsillar hypertrophy causing airway or swallowing obstruction;
- suspicion of malignancy.
Surgical Treatment
The standard approach is tonsillectomy (complete removal of the tonsils) using either cold dissection or advanced techniques such as radiofrequency, laser, or coblation. The choice depends on clinical presentation, patient age, and surgeon’s expertise.
KindCare Medical Center — “First Violin” in Protecting Your Tonsils
At KindCare, we follow international guidelines and tailor our protocols to each patient:
- ENT Specialist — Dr. Maryna, PhD, Associate Professor, 25 years of experience, performs detailed diagnostics, endoscopic examinations, and tonsil irrigation.
- Pediatrician — Dr. Irina, over 25 years of experience, ensures overall child health, immunity support, and sore throat prevention.
- Comprehensive diagnostic services: endoscopy, cultures, laboratory tests.
- Conservative and surgical treatments in line with the latest medical standards.
Book a consultation at KindCare Medical Center — we’ll preserve your tonsils’ health or remove them safely and effectively if needed.